Biofuel breakthrough: HyFlexFuel converts sewage sludge into kerosene
The EU-funded HyFlexFuel research project has recently succeeded in producing biofuels via hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) from a variety of biomasses, including sewage sludge, food waste, manure, wheat straw, corn straw, pine sawdust, miscanthus, and microalgae, in a pilot-scale continuous HTL plant at Aarhus University (Denmark). “It was a real milestone for HyFlexFuel to demonstrate biofuel production from such a variety of feedstocks at the hundred-kilogram scale,” says Patrick Biller, who leads pilot-scale HTL research at Aarhus University. Biocrudes from three representative feedstocks, spirulina (microalgae), sewage sludge, and wheat straw, were further refined into a mixture of hydrocarbon fuels at Aalborg University (Denmark). “Thanks to the expertise of several project partners, HyFlexFuel has proven that HTL biofuels can be successfully upgraded to drop-in fuels in an industrially relevant environment, achieving hundreds of hours of continuous operation,” adds Daniele Castello from Aalborg University. Analyses of the kerosene fractions of the upgraded biofuel show promising compositions for use as aviation fuel. “The production of HTL fuels from three different classes of feedstock demonstrates the flexibility of the process,” says project coordinator Valentin Batteiger of Bauhaus Luftfahrt (Germany). “Meeting jet fuel specifications is an appropriate target to validate that high-performance transportation fuels can indeed be produced from a wide range of residual and waste streams through hydrothermal liquefaction.”
HTL as the key to sustainable biofuel production
Decarbonization of the transportation sector will require large amounts of renewable fuels. So far, renewable diesel and jet fuels are mainly derived from vegetable oils, but the EU Renewable Energy Directive restricts the use of biofuels from food and feed crops because they do not meet sustainability requirements when produced on a large scale. Going forward, it will be important to commercialize advanced biofuel conversion technologies that utilize a broader and more sustainable feedstock base.
The HTL process
Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) is an emerging biofuel technology for producing transportation fuels from a variety of biowastes and other biomasses.
HTL has several key advantages, the most important of which are:
- Flexible production potential: HTL conversion technology taps into a vast global bio-resource with a local diversity of primary biomasses. The technology is compatible with a wide range of organic wastes and residues, lignocellulosic energy crops or aquatic biomasses, and can be adapted to specific regional feedstock availability.
- Cost-effectiveness: it can produce advanced biofuels, from marine fuels to kerosene, potentially at a lower cost than most competing renewable fuel pathways.
- Sustainability: HTL technology has the potential to produce fuels with a low lifecycle carbon footprint without competing with food and feed production. It has the potential to recycle waste streams and thus contribute to a circular economy.
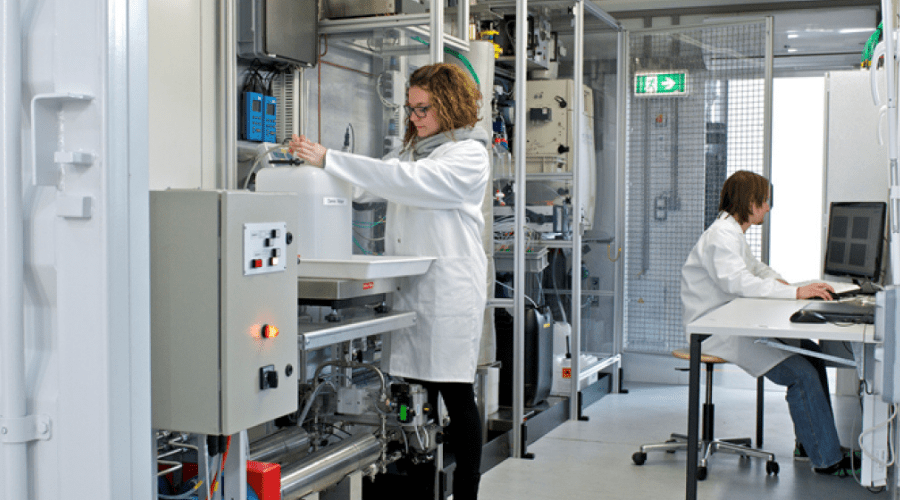
The pilot-scale HTL plant processes aqueous biomass slurries (~20% dry solids) at temperatures up to 350°C and pressures around 200 bar, where the water does not boil but remains in the liquid state. Under these conditions, the biomass is converted into a crude bio-oil, which is separated from the process water downstream of the reactor. In a second step, the HTL bio-oil is refined into transportation fuel products by catalytic treatment with hydrogen at high temperature and pressure (hydrotreating). This removes oxygen and nitrogen from the biocrude, which in turn is converted to a mixture of hydrocarbons. Distillation of the processed HTL biofats yields drop-in fuels in the gasoline, kerosene and diesel range.
Laboratory demonstration of the most important process steps by European consortium
As part of the EU HyFlexFuel project, all key steps along an HTL fuel production chain are being investigated at the premises of several European research institutions and companies. The potential availability of residual and waste streams across Europe is analyzed by the DBFZ, the German Institute for Biomass Research, using a geospatial approach. Aarhus University is further developing and optimizing HTL conversion on a laboratory scale and transferring the results to a pilot-scale continuous HTL plant, where all samples for downstream processes are also produced. Aalborg University, with the support of Haldor Topsøe (Denmark), realized the upgrading of various biofats to transportation fuels by catalytic hydrotreatment, while Eni (Italy) investigated the perspective of co-processing HTL biofats in conventional petroleum refineries.
Solid particles and process waters, which are also generated during HTL conversion, contain a significant amount of the carbon and nutrients from the original biomass. Two options for producing biogas from the organic components of these process waters are being investigated by the Paul Scherrer Institute (Switzerland) using catalytic hydrothermal gasification on their Energy System Integration Platform and by OWS (Belgium) using anaerobic digestion. Phosphorus recovery is particularly important for HTL of sewage sludge to close nutrient cycles. The University of Hohenheim (Germany) has demonstrated the precipitation of struvite, a fertilizer product, from HTL solids and process waters. Bauhaus Luftfahrt is coordinating the project and analyzing the economic and environmental impact of HTL fuel production. ARTTIC Innovation GmbH (Germany) serves as project management partner and supports dissemination activities.
Towards approval of HTL kerosene for civil aviation
To date, seven alternative fuel production routes have been approved as blending components for commercial aviation by the ASTM D-7566 specification [1]. The HyFlexFuel consortium is preparing for the approval of HTL kerosene in collaboration with key partners in Europe and the US. Kerosene samples from the HyFlexFuel project were analyzed by the H2020 project JETSCREEN (coordinated by DLR, Germany) and the University of Dayton. The results show that all basic physicochemical properties of kerosene, such as energy density or cold flow properties, are already met, while the concentration of certain trace components needs to be further reduced to meet the stringent specifications for kerosene.
[1]: Standard specification for jet fuel containing synthetic hydrocarbons.
Project background
HyFlexFuel is a four-year project (10/2017 – 9/2021) funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. Leading European research organizations and companies in the field of HTL research are participating in HyFlexFuel, namely Aarhus University, Aalborg University, Paul Scherrer Institute, University of Hohenheim, DBFZ Deutsches Biomasseforschungszentrum gemeinnützige GmbH, Haldor Topsøe, Eni and OWS. Bauhaus Luftfahrt e.V. coordinates the project and ARTTIC Innovation GmbH supports the research consortium with project management and communication.
For more information, visit www.hyflexfuel.eu.
Why the carousel of amendments to the R&D tax credit law continues to turn
The R&D tax credits in 2024The year 2024 has proven to be decisive for the German R&D tax credits. Following the most recent amendment as part of the Growth Opportunities Act in March, the Federal Government realized during the budget consultations for 2025...
Register Now: In Conversation with EBiSC2
Unlocking the Potential of Stem Cells: Discover the EBiSC Journey to SustainabilityJoin the conversation on the initiative that’s shaping the future of biomedical research! On May 15, 2024, from 14:15 to 15:00 CEST (Europe/Brussels time), the Innovative Health...
The R&D tax credit with a blind eye to earnings –
Why loss-making companies (wrongly) hesitate
Recapitulation The German R&D tax credit has become much more popular in recent years after a modest response following the introduction of the instrument. This can be seen not only in advertising and studies by various associations, but also in the bare figures...
Junior Funding Consultant (m/f/d)
We offer you the unique opportunity to become part of a successful & young team in the attractive growth market for tax-incentivised research funding (R&D tax credits). We are looking for Junior Funding Consultants with a passion for innovation, scientific...
First successful demonstration with 100% green H2
HYFLEXPOWER celebrates successful operation of a gas turbine with 100% green H2On October 12, 2023, at a public event hosted at the HYFLEXPOWER demonstrator site in Saillat-sur-Vienne, France, the HYFLEXPOWER consortium unveiled a ground-breaking achievement - the...
New Security Project AGILE Will Improve Disaster Risk Management
New international security project to improve disaster risk management for unexpected eventsThe international security project AGILE will kick start today. The project is to develop novel tools and methodologies for understanding, anticipating, and managing High...
SYNERGISE for Improved Disaster Management
Internationally Funded Project to Develop an Integrated Toolkit for Improved Management of Natural and Man-Made Disasters Kicks-Off TodayTo boost the efficiency and safety of first responders during life-saving missions, the SYNERGISE team will develop a Novel...
Junior Innovation Consultant (m/f/d)
We offer you the unique opportunity to become part of a dynamic team in the attractive field of innovation and research. We are looking for Innovation Consultants with a passion for innovation, scientific writing and project management. This position is for recent...
Senior Innovation Consultant (m/f/d)
We offer you the unique opportunity to become part of a dynamic team in the attractive field of innovation and research. We are looking for specialists with a passion for innovation, scientific writing and project management. This position is for experienced...
Business Developer (m/f/d)
We are looking for specialists in business development with a strong sales talent and an interest in innovation, research and science. This position is for recent graduates or experienced professionals and involves assisting clients from a variety of industries with...